Elementary Report Card Information
Page Navigation
Fourth Grade Report Card Overview
-
Interpreting the Grade-Plus Report Card for Fourth Grade
Grade-Plus Report CardThe Grade Plus report card for 4th grade provides a detailed analysis of a student's academic achievements. For English Language Arts (ELA) and Math, students receive an overall percentage grade and a breakdown of their performance in specific content areas within these subjects. This detailed feedback highlights both strengths and areas needing improvement. For Science and Social Studies, teachers report grades using a percentage score.Academic Performance IndicatorsIn addition to the numeric percentage grade in ELA and Math, students will receive an analysis of their performance by standard domain, enabling them to identify areas of academic strength and opportunities for improvement more readily. The indicators are defined as follows:Below Standard (1): The student requires more support, frequent re-teaching, and additional practice to understand the content.
Approaching Standard (2): The student is applying learned skills but needs some teacher support to meet grade-level expectations fully.
Meets Standard (3): The student is performing at grade level, producing quality work with little to no teacher support, and fulfilling grade-level expectations.
Exceeds Standard (4): The student works above grade level, consistently producing outstanding, independent work.
X: Not assessed at this time.* For additional information, see the Individualized Education Program (IEP) progress report.
Work Habit Indicators
Cultivating effective work habits is essential for a student's success. The indicators for work habits are:
Exemplary (E): Performance is beyond grade-level expectations.Successful (S): Performance meets grade-level expectations.
Needs Improvement (N): Performance needs improvement to meet grade-level expectations.
Content Area Descriptors
To enhance communication about assessed skills and knowledge, our district content specialists provide descriptors for each category on the report card. Expand each content area to view the detailed descriptors.
-
English Language Arts
Reading Foundational Skills
- Phonics and Spelling
- Use combined knowledge of all letter-sound correspondences, syllabication patterns, and morphology (roots and affixes) to read accurately
- Use combined knowledge of all letter-sound correspondences, syllabication patterns, and morphology (roots and affixes) to read accurately
- Fluency
- Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension
- Vocabulary
-
- Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening
- Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases
- Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and word nuances
- Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversations, general, academic, and domain-specific vocabulary
Interpreting Texts
- Listening Comprehension
- Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions on grade 3 topics and texts
- Paraphrase portions of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally
- Identify the reasons and evidence a speaker provides to support particular points
- Reading Comprehension
- Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences from a fiction text
- Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences from a nonfiction text
- Determine a theme of a story, drama, or poem from details in the text; summarize the text
- Determine the main idea of a non-fiction text and explain how it is supported by key details; summarize the text
- Describe in depth a character, setting, or event in a story or drama, drawing on specific details in the text
- Explain events, procedures, ideas, or concepts in a historical, scientific, or technical text, including what happened and why, based on specific information in the text
- Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including those that allude to significant characters found in mythology
- Determine the meaning of general academic language and domain-specific words or phrases in a text relevant to a grade 4 topic or subject area
- Explain major differences between poems, drama, and prose, and refer to the structural elements of poems (e.g., verse, rhythm, meter) and drama (e.g., casts of characters, settings, descriptions, dialogue, stage directions) when writing or speaking about a text
- Describe the overall structure (e.g., chronology, comparison, cause/effect, problem/solution) of events, ideas, concepts, or information in a text or part of a text
- Compare and contrast the point of view from which different stories are narrated, including the difference between first- and third-person narrations
- Compare and contrast a firsthand and secondhand account of the same event or topic; describe the differences in focus and the information provided
- Make connections between the text of a story or drama and a visual or oral presentation of the text identifying similarities and differences
- Interpret information presented visually, orally, or quantitatively (e.g., in charts, graphs, diagrams, time lines, animations, or interactive elements on Web pages) and explain how the information contributes to an understanding of the text in which it appears
- Explain how an author uses reasons and evidence to support particular points in a text
- Compare and contrast the treatment of similar themes and topics (e.g., opposition of good and evil) and patterns of events (e.g., the quest) in stories, myths, and traditional literature from different cultures
- Integrate information from two texts on the same topic in order to write or speak about the subject knowledgeably
Constructing Texts
- Oral Communication
- Report on a topic or text, tell a story, or recount an experience in an organized manner, using appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details to support main ideas or themes; speak clearly at an understandable pace.
- Add audio recordings and visual displays to presentations when appropriate to enhance the development of main ideas or themes.
- Differentiate between contexts that call for formal English (e.g., presenting ideas) and situations where informal discourse is appropriate
- Written Communication
- Write opinion pieces
- Write informative (explanatory) texts
- Write narratives (stories)
- Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development and organization are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience
- With guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, and editing
- With some guidance and support from adults, use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing as well as to interact and collaborate with others; demonstrate sufficient command of keyboarding skills to type a minimum of one page in a single sitting
- Conduct short research projects that build knowledge through investigation of different aspects of a topic
- Recall relevant information from experiences or gather relevant information from print and digital sources; take notes and categorize information, and provide a list of sources
- Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research
- Demonstrate command of the conventions of English grammar and usage when writing and speaking
- Demonstrate command of the conventions of English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing
- Phonics and Spelling
-
Mathematics
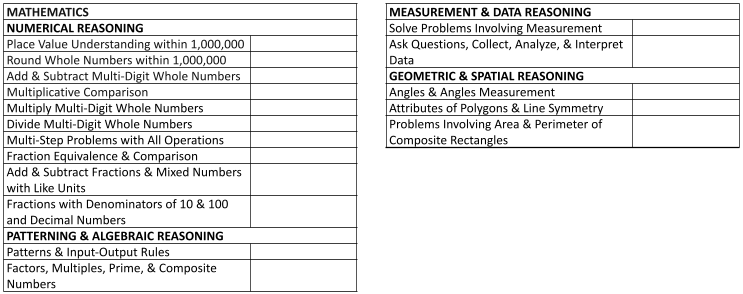
Numerical Reasoning
- Place Value Understanding within 1,000,000
- Read and write multi-digit whole numbers in unit, standard, and expanded form (Q1)
- Explain the relationship between a digit in a multi-digit whole number and the same digit in the place to the right and left using multiplication and division (Q1)
- Compare up to three whole numbers by using >, =, or < (Q1)
- Order up to five whole numbers (Q1)
- Round Whole Numbers within 1,000,000
- Round multi-digit whole numbers within 1,000,000 (Q1)
- Add & Subtract Multi-Digit Whole Numbers
- Add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers by using place value understanding and algorithms (Q1)
- Multiplicative Comparison
- Model multiplicative comparison statements (Q1)
- Create two comparison statements, given a multiplication equation (Q1)
- Write multiplicative comparison statements as multiplication equations (Q1)
- Solve word problems involving multiplicative comparison by using multiplication or division within 100 (Q1)
- Multiply Multi-Digit Whole Numbers
- Multiply a two-digit whole number by a one-digit whole number using place value understanding and strategies (Q2)
- Multiply whole numbers of up to four digits by one-digit whole numbers using place value understanding and strategies (Q2)
- Multiply 2 two-digit whole numbers using place value understanding and strategies (Q3)
- Divide Multi-Digit Whole Numbers
- Divide by a one-digit whole number using tens and ones using place value understanding and strategies (Q2)
- Divide whole numbers of up to four digits by one-digit whole numbers using place value understanding and strategies (Q2)
- Use context to determine how to interpret a remainder (Q3)
- Multi-Step Problems with All Operations
- Solve multi-step word problems by using addition and subtraction; represent these problems by using equations (Q1)
- Solve multi-step word problems by using the four arithmetic operations, including problems that require interpreting remainders in context, represent these problems by using equations, and assess the reasonableness of answers (Q3)
- Assess the reasonableness of estimates when using rounding as an estimation strategy (Q1 - Q4)
- Fraction Equivalence & Comparison
- Generate equivalent fractions and their representations (Q3)
- Model and explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n × a)/(n × b) (Q3)
- Compare two fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator and justify the conclusion by using a visual fraction model (Q3)
- Compare two fractions with different numerators and different denominators and justify the conclusions (Q3)
- Add & Subtract Fractions & Mixed Numbers with Like Units
- Decompose whole numbers and fractions as the sum of unit fractions (Q3)
- Decompose fractions into a sum of fractions with the same denominator in more than one way (Q3)
- Add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers with like denominators (Q3)
- Fractions with Denominators of 10 & 100 and Decimal Numbers
- Express fractions with denominator 10 as equivalent fractions with denominator 100 (Q4)
- Represent tenths and hundredths in decimal form, fraction form, or by using a model (Q4)
- Compare two decimal numbers to hundredths and justify the conclusions (Q4)
Patterning & Algebraic Reasoning
- Patterns & Input-Output Rules
- Create a pattern that follows a given rule and identify additional features of that pattern (Q2)
- Use input-output tables to represent patterns and solve problems (Q2)
- Factors, Multiples, Prime, & Composite Numbers
- Identify a multiple of a given whole number in the range 1–100 (Q2)
- Find whole-number factor pairs in the range 1–100 (Q2)
- Determine whether a whole number up to 100 is prime or composite (Q2)
Measurement & Data Reasoning
- Solve Problems Involving Measurement
- Solve multiplicative comparison word problems that involve units of measurement (Q1)
- Represent measurement quantities by using diagrams (Q1)
- Solve word problems that require expressing measurements of larger units of length in terms of a smaller unit within the customary system (Q1)
- Express larger/smaller units of time, metric units of weight, and liquid volumes in terms of a smaller/larger unit by using tables (Q3)
- Solve word problems that require expressing measurements of larger/smaller units of time, metric units of weight, and liquid volumes, in terms of a smaller/larger unit (Q3)
- Solve measurement addition and subtraction word problems involving fractions with like denominators (Q3)
- Solve measurement word problems that involve adding decimal fractions with denominators of 10 and/or 100 (Q4)
- Ask Questions, Collect, Analyze, & Interpret Data
- Create a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, 1/8) and solve problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions by using the line plot (Q3)
- Conduct a real-life investigation, collect and represent data, and ask and answer questions based on a graphical display (Q4)
Geometric & Spatial Reasoning
- Angles & Angle Measurement
- Identify and draw right, acute, and obtuse angles in relation to an angle measuring 90 degrees (Q4)
- Apply understanding of angle types to classify triangles as acute, obtuse, or right (Q4)
- Convert between angle measures expressed as a fractional turn through a circle and degrees using division or missing factor equation (Q4)
- Measure angles in reference to 360 degrees in a circle using non-standard units of measurement (Q4)
- Attributes of Polygons & Line Symmetry
- Identify points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), perpendicular and parallel lines, and lines of symmetry in two-dimensional figures (Q4)
- Identify and draw angles (right, acute, obtuse) in a variety of contexts (Q4)
- Identify attributes and use them to classify two-dimensional figures, including triangles (Q4)
- Problems Involving Area & Perimeter of Composite Rectangles
- Solve problems involving area of rectangles and composite rectangles (Q2)
- Solve problems involving perimeter of rectangles and composite rectangles (Q2)
- Place Value Understanding within 1,000,000
-
Science
Earth Science (Q1 & Q3)
- Ask questions - to compare and contrast technological advances that have changed the amount and type of information on distant objects in the sky (Q1)
- Construct an argument - on why some stars (including the Earth’s sun) appear to be larger or brighter than others (Q1)
- Construct an explanation - of the differences between stars and planets
- Evaluate the strengths and limitations of models of our solar system in describing the relative size, order, appearance, and composition of planets and the sun (Q1)
- Develop a model to support an explanation of why the length of day and night change throughout the year (Q1)
Develop a model based on observations to describe the repeating pattern of the phases of the moon (new, crescent, quarter, gibbous, and full) (Q1) - Construct an explanation of how the Earth’s orbit, with its consistent tilt, affects seasonal changes (Q1)
- Plan and carry out investigations to observe the flow of energy in water as it changes states from solid (ice) to liquid (water) to gas (water vapor) and changes from gas to liquid to solid (Q3)
- Develop models to illustrate multiple pathways water may take during the water cycle (evaporation, condensation, and precipitation) (Q3)
- Construct an explanation of how weather instruments (thermometer, rain gauge, barometer, wind vane, and anemometer) are used in gathering weather data and making forecasts (Q3)
- Interpret data from weather maps, including fronts (warm, cold, and stationary), temperature, pressure, and precipitation, to make an informed prediction about tomorrow’s weather (Q3)
- Ask questions and use observations of cloud types (cirrus, stratus, and cumulus) and data of weather conditions to predict weather events (Q3)
Construct an explanation based on research to communicate the difference between weather and climate (Q3)
Life Science (Q2)
- Develop a model - to describe the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers in a community
- Develop simple models - to illustrate the flow of energy through a food web/food chain, beginning with sunlight and including producers, consumers, and decomposers
- Design a scenario - to demonstrate the effect of a change on an ecosystem
- Develop a model - Illustrating and describing changes to the flow of energy in an ecosystem when plants or animals become scarce, extinct, or overabundant using printed and digital media
Physical Science (Q4)
- Plan and carry out investigations to observe and record how light interacts with various materials to classify them as opaque, transparent, or translucent
- Plan and carry out investigations to describe the path light travels from a light source to a mirror and how it is reflected by the mirror using different angles
- Plan and carry out an investigation utilizing everyday materials to explore examples of when light is refracted
- Plan and carry out an investigation utilizing everyday objects to produce sound and predict the effects of changing the strength or speed of vibrations
- Design and construct a device to communicate across a distance using light and/or sound
- Plan and carry out an investigation on the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces on an object and communicate the results
- Construct an argument to support the claim that gravitational force affects the motion of an object
- Ask questions to identify and explain the uses of simple machines (lever, pulley, wedge, inclined plane, wheel and axle, and screw) and how forces are changed when simple machines are used to complete tasks
-
Social Studies
Geographic Understandings (Q1)
- Locate important physical and man-made features in the United States
- Describe how physical systems affect human systems
Historical Understandings (Q1 - Q4)
- Explain the causes, events, and results of the American Revolution (Q1)
- Analyze the challenges faced by the framers of the Constitution (Q2)
- Explain westward expansion in America (Q2 & Q3)
- Examine the main ideas of the abolitionist and suffrage movements (Q3)
- Explain the causes, major events, and consequences of the Civil War (Q3 & Q4)
- Analyze the effects of Reconstruction on American life (Q4)
Government/Civic Understandings (Q1)
- Describe the meaning of "natural rights" as found in the Declaration of Independence, “We the People” from the Preamble to the US Constitution as a reflection of the consent of the governed or popular sovereignty, the federal system of government in the US (federal powers, state powers, and shared powers), and representative democracy/republic (Q1)
- Explain the importance of freedoms guaranteed by the First Amendment to the US Constitution (Q1)
- Describe the structure of government and the Bill of Rights (Q1)
Economic Understandings (Q1 & Q3)
- Identify the elements of a personal budget (income, expenditures, and saving) and explain why personal spending and saving decisions are important (Q1)
- Describe the basic economic concepts of trade, opportunity cost, specialization, voluntary exchange, productivity, and price incentives to illustrate historical events (Q3)
-
Sample Fourth Grade Report Card


